SGN-2506 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Fall 2006 Exam 1-Dec-2006
|
|
|
- Tero Parviainen
- 8 vuotta sitten
- Katselukertoja:
Transkriptio
1 SGN-2506 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Fall 2006 Exam -Dec-2006 Perform five (no more!) freely chosen problems of Problems -6. Each of them is worth of 6 points. No literature. Needed formulas are given in context. Use of functional calculator allowed. In order to use a programable calculator, you must let the examination supervisor clear its memory at the beginning of the exam! Problems:. Decide, whether the following statements are true or false. If you do not know the answer, answer. Simply answer only either True, False, or. No additional explanations are needed! Each correct answer gives + point, and each wrong answer gives - point. No answer ( ) is worth of 0 points. The absolute minimum score of the problem is 0 points even if you answer wrongly to each statement a) f). a) The density p(x θ) is identifiable, if there exist such different values θ θ of the parameter θ that for any given feature value x it holds p(x θ) p(x θ ). b) The components of the multinormal random vector are independent if the covariance matrix of its distribution is a diagonal matrix. c) Any continuous function defined on the real line R defines a probability density function if and only if the integral of the function over R is equal to. d) The decision regions of non-linear discriminant functions need not to be convex. e) The expectation-maximization algorithm can be applied (reasonably) also in such situations, where the global maximum of the likelihood does not exist. f) The gradient of the perceptron criterion functionj p, J p (a) = y Y(a) y, is constant with respect to the augmented weight vector a of the corresponding linear discriminant function. 2. Consider a three category k-nearest neighbor classifier and the following set of two-dimensional labeled prototypes: ω (4,4) (4,7) (8,6) (7,4) (4,9) (6,2) (2,6) ω 2 (-7,8) (3,) (-2,-) (4,3) (3,4) (4,-3) (0,6) ω 3 (3,2) (8,) (3,3) (6,3) (5,0) (3,9) (,7) Classify the point (4,4) based on (a) the nearest neighbor rule
2 (b) The 3-nearest neighbor rule (c) The 7-nearest neighbor rule Measure distances using the L -metric: d (a,b) = max a i b i. i Correct answers without explanation how you have obtained them will be worth of zero points; so, explain how you got the answers! 3. a) Consider a linear machine with discriminant functions g i (x) = w t x + w i0, i =,...,c. Show that the decision regions are convex by showing that if x R i and x 2 R i then λx + ( λ)x 2 R i for 0 λ. b) Consider the set of feature vectors { [ ] [ [ [ 0 0 } D =,,, 0 0] ] ] and the classes ω = { [ ] 0, 0 [ ] }, ω 2 = { [ ] 0, [ ] } 0 Show that ω and ω 2 are not linearly separable, that is, show that there are no line separating ω and ω Consider a univariate two-class classification problem. You have collected a feature data D = D D 2, where the features D = {.6,.8, 2., 2.2, 2.7, 2.8, 3.0, 3.2, 3.5} have been measured from the objects known to belong to the class ω and the features D 2 = {2.3, 3., 3.3, 3.4, 3.6, 3.8, 4.4} have been measured from the objects known to belong to the class ω 2. A new object is chosen and the feature value 3.5 is measured. Classify this object. Instruction: Let the window function be { u /2 ϕ(u) = 0 otherwise Estimate the class conditional densities with the Parzen window estimator of the form p n (x) = n ϕ( x x i ) n V n h n i= with h n =.2. Estimate also the prior probabilities P(ω ) and P(ω 2 ) based on the training data D. Thereafter, apply the Bayes minimum error rate classification rule to p n and to the estimated prior probabilities. (Remember the Bayes rule: P(ω x) = P(ω)p(x ω) ) p(x) 2
3 5. Let x = (4, 5) T,x 2 = (, 4) T,x 3 = (0, ) T,x 4 = (5, 0) T, and consider the following three partitions. (a) D = {x,x 2 }, D 2 = {x 3,x 4 } (b) D = {x,x 4 }, D 2 = {x 2,x 3 } (c) D = {x,x 2,x 3 }, D 2 = {x 4 } Which of these does the sum-of-squared errors criterion (the K-means criterion) favor? (Remember the sum-of-squared errors criterion: J({µ,...,µ c }) = c i= x D i x µ i 2 ) 6. In many pattern classification problems one has the option either to assign the pattern to one of the c classes or to reject it as being unrecognizable. If the cost for rejects is not too high, rejection may be a desirable action. Let 0 i = j, i, j =,...,c λ(α i ω j ) = λ r i = c +, λ s otherwise where λ r is the loss incurred for choosing the c + th action, rejection, and λ s is the loss incurred for making any substitution error. Show that minimum risk is obtained if we decide ω i if P(ω i x) P(ω j x) for all j i and if P(ω i x) λ r /λ s and reject otherwise. What happens if λ r = 0? What happens if λ r > λ s? (Remember the formula R(α i x) = c λ(α i ω j )P(ω j x)) j= 3
4 SGN-2506 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Fall 2006 Exam 26-Feb-2007 Perform five (no more!) freely chosen problems of Problems -6. Each of them is worth of 6 points. No literature. Needed formulas are given in context. Use of functional calculator allowed. In order to use a programable calculator, you must let the examination supervisor clear its memory at the beginning of the exam! Problems:. Decide, whether the following statements are true or false. If you do not know the answer, answer. Simply answer only either True, False, or. No additional explanations are needed! Each correct answer gives + point, and each wrong answer gives - point. No answer ( ) is worth of 0 points. The absolute minimum score of the problem is 0 points even if you answer wrongly to each statement a) f). a) The Parzen density estimator is a non-parametric method to estimate also continuous densities based on finite data records. b) The density p(x θ) is identifiable, if there exist such different values θ θ of the parameter θ that for any given feature value x it holds p(x θ) p(x θ ). c) The K-means algorithm belongs to the unsupervised classification methods. d) The lower the training error, the lower the classification error also for newcoming features. e) Introducing new features to the classification system, that is extending the feature space, the Bayes (classification) error can be decreased. f) Defining L : R 2 {0, }, L(x, y) = { 0, x = y,, x y, one can prove that L is a metric. 2. The random variables X and Y possess the joint uniform density over the region depicted (in black) in Figure below. Find a) the expression for the joint density f (X,Y ) (x, y); Hint: whenever both x and y belong to the black region, the joint density function f (X,Y ) (x, y) takes a positive constant value and vanishes otherwise. b) the expression for the marginal density f X (x); c) the expression for the conditional density f Y X (y x); d) Are X and Y independent? Explain briefly, how you deduced the answers. Hint: You do not have to integrate anything.
5 Figure : The random variables X and Y in Problem 2 have the joint uniform distribution over the black region. That is, whenever both x and y belong to the black region, the joint density function f (X,Y ) (x, y) takes a positive constant value and vanishes otherwise. 3. Suppose a two-class classification problem with the priors P(ω ) = 0.3 and P(ω 2 ) = 0.7. Suppose further the uniform class-conditional distributions on the closed hyper-interval [a i,b i ], p(x ω i ) = { vol([a i,b i]), if a i x b i, i =, 2, 0, otherwise, where vol([a i,b i ]) is the volume of [a i,b i ] and is operated componentwise. Compute the Bayes error. Explain and write down the needed computational steps. (The Bayes error, P(error): P(error) = P(error x)p(x)dx, where P(error x) is the probability of misclassification given the feature value x and the integration is performed over the whole feature space (i.e. all possible feature values x.) The Bayes rule, in turn, is given by and the volume of a hyper-interval by P(ω x) = p(x ω)p(ω), p(x) vol([c,d]) = l (d j c j ), j= 2
6 where l is the dimension of the vectors c and d.) 4. Consider a three category k-nearest neighbor classifier and the following set of two-dimensional labeled prototypes: ω (-2,-2) (2,) (0,-) (0,0) (3,0) (3,) (5,0) ω 2 (-,0) (0,-) (-,-) (4,2) (,4) (4,-) (,) ω 3 (-2,-2) (,-6) (3,-3) (0,-2) (2,0) (0,9) (-,3) Classify the point (,) based on (a) the nearest neighbor rule, (b) the 3-nearest neighbor rule, (c) the 5-nearest neighbor rule, and (d) The 7-nearest neighbor rule Measure distances using the Mahalanobis metric: L Mahalanobis,C (a,b) = (a b)c (a b) T, where [ 4 ] C = and a and b are (here) 2-dimensional row vectors. Correct answers without explanation how you have obtained them will be worth of zero points; so, explain how you got the answers! 5. Let a one-dimensional classification task consist of c different classes, ω, ω 2,...,ω c, each obeying either exponential or normal class conditional density. Prove that the Bayes minimum error rate classifier can be identified with at most quadratic discriminant functions g i (x), i =, 2,..., c, that is, each g i (x) can be expressed in the form g i (x) = w i2 x 2 + w i x + w i0, where w i2, w i and w i0 are scalars. (The exponential density function: { θ exp( θx) if x 0 p(x θ) = 0 otherwise and normal density function: p(x [µ, σ]) = 4 3 2πσ 2 exp ( 2 (x µ)2 /σ 2).) 6. a) Consider the following six training samples from the classes ω and ω 2 : ω : (, 2) T (2, 4) T ( 3, ) T ω 2 : (2, 4) T (, 5) T (5, 0) T 3
7 Are they linearly separable? Explain. b) Compute the value of the perceptron criterion function for the above six training samples at a = (0, 0, ) T. Starting from a = (0, 0, ) T take a single step of the perceptron algorithm with the learning rate η(k) =. Remember to augment and normalize the feature vectors. (Perceptron criterion function: where Y(a) = {y a T y < 0}.) J p (a) = y Y(a) a T y, 4
8 SGN-2500 Johdatus hahmontunnistukseen Kevät 2007 SGN-2506 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Fall 2006 Tentti / Exam 24-Sep-2007 Tentti on kaksikielinen: kysymykset esitetään sekä suomeksi että englanniksi. Voit vastata kummalla kielellä haluat. Exam is bilingual: Problems are stated both in Finnish and in English. You may answer with either language. Vastaa viiteen (ei kuuteen!) vapaavalintaiseen tehtävään Tehtävistä -6. Jokaisen maksimipistemäärä on 6 pistettä. Ei kirjallisuutta. Tarvittavat kaavat annetaan tehtävien yhteydessä. Funktiolaskin sallittu. Jos haluat käyttää ohjelmoitavaa laskinta, tentinvalvojan on annettava tyhjentää laskimen muisti tentin alussa! Perform five (no more!) freely chosen problems of Problems -6. Each of them is worth of 6 points. No literature. Needed formulas are given in context. Use of functional calculator allowed. In order to use a programable calculator, you must let the examination supervisor clear its memory at the beginning of the exam! Tehtävät: Problems:. Ovatko seuraavat väitteet tosia vai epätosia? Ellet tiedä vastausta, vedä viiva. Vastaa pelkästään joko Tosi, Epätosi tai. Mitään lisäselityksiä ei tarvita! Jokaisesta oikeasta vastauksesta saat + pisteen ja jokaisesta väärästä vastauksesta - pisteen. Vastaamatta jättämisestä ( ) saat 0 pistettä. Tehtävän minimipistemäärä on 0 pistettä, vaikka vastaisit väärin kaikkiin väitteisiin a) f). Decide, whether the following statements are true or false. If you do not know the answer, answer. Simply answer only either True, False, or. No additional explanations are needed! Each correct answer gives + point, and each wrong answer gives - point. No answer ( ) is worth of 0 points. The absolute minimum score of the problem is 0 points even if you answer wrongly to each statement a) f). a) Bayes-(minimivirhe)luokittajaa vastaava erotinfunktio on lineaarinen (piirrevektorin suhteen). Tosi/Epätosi/ The corresponding discriminant function of the Bayes (minimum error rate) classifier is linear (with respect to the feature vector). b) Tiheysfunktio p(x θ) on tunnistettavissa, jos on olemassa sellaiset eri parametriarvot θ θ, että joka piirteelle x on p(x θ) p(x θ ). Tosi/Epätosi/ The density p(x θ) is identifiable, if there exist such different values θ θ of the parameter θ that for any given feature value x it holds p(x θ) p(x θ ). c) Suurimman uskottavuuden menetelmä on ei-parametrinen keino havaitun datan tiheysfunktion estimoimiseksi. Tosi/Epätosi/ The Maximum likelihood method is a non-parametric way to estimate density functions based on observed data.
9 d) Perceptron -algoritmi pyrkii minimoimaan opetusvirheen. Tosi/Epätosi/ The Perceptron algorithm tries to minimize the training error. e) Yleinen dataan D perustuva tiheysestimaattori on p n (x) = k/(nv ), missä V on x:n ympärille muodostetun alueen B tilavuus, n on datan D pisteiden kokonaislukumäärä ja k on alueeseen B kuuluvien datapisteiden lukumäärä.. Tosi/Epätosi/ The general density estimator p n (x) based on the data D is defined as p n (x) = k/(nv ), where V is the volume of the region B around x, n is the total number of data points in D, and k is the number of the data points enclosed by B. f) Normaalijakautuneiden luokkien erotinfunktiot ovat enintään neliöllisiä. Tosi/Epätosi/ We can find for normally distributed classes the discriminant functions beeing at most quadratic. 2. Jatkuva satunnaismuuttuja X mittaa erään systeemin komponentin lämpötilaa (Celsius-asteissa). X noudattaa alla annettua jatkuvaa tiheysfunktiota f: The continuous random variable X measures the temperature (in o C degrees) of a component of a system and X possesses the continuous density { c exp(a x ) jos/if x a f(x) = 0 jos/if x < a Olkoon a kiinnitetty vakio. Määrää vakio c siten, että f on tiheysfunktio. Laske vielä todennäköisyys, että komponentin lämpötila on alle 0 o C astetta. Consider a as a fixed constant. Determine the constant c such that f is a density function. Thereafter, compute the probability that the temperature of the component is below zero degrees in Celsius. 3. Ajatellaan kolmen luokan k:n lähimmän naapurin luokittajaa ja allaolevaa 2- dimensioista opetusdataa: Consider a three category k-nearest neighbor classifier and the following set of two-dimensional labeled prototypes: ω (4,4) (4,7) (8,6) (7,4) (4,9) (6,2) (2,6) ω 2 (-7,8) (3,) (-2,-) (4,3) (3,4) (4,-3) (0,6) ω 3 (3,2) (8,) (3,3) (6,3) (5,0) (3,9) (,7) Luokita piste (4,4) käyttäen / Classify the point (4,4) based on (a) lähimmän naapurin sääntöä / the nearest neighbor rule, (b) kolmen lähimmän naapurin sääntöä / the 3-nearest neighbor rule, 2
10 (c) seitsemän lähimmän naapurin sääntöä / the 7-nearest neighbor rule. Etäisyydet käyttäen L -metriikkaa / Measure distances using the L -metric: d (a,b) = max a i b i. i 4. Olkoon n:n näytteen joukko D jaettu erillisiin osajoukkoihin D,...,D c, missä c < n. Jos jokin tämän jaon jäsen, sanotaan D i on tyhjä joukko, ei otoskeskiarvo µ i ole määritelty. Todista, ettei kriteerifunktion J e = x µ i 2 D i x D i minimoivaan jakoon kuulu tyhjää joukkoa. If a set of n samples D having different values is partitioned into c < n disjoint subsets D,..., D c the sample mean µ i is undefined if the set D i is empty. Show that the partition minimizing the sum-of-squared errors J e = x µ i 2 D i x D i includes no empty sets. Vihje: Olkoon annettuna jako, jossa on mukana tyhjä joukko. Silloin on olemassa myös sellainen jako, jossa ei ole mukana tyhjää joukkoa ja tuon jaon kriteerifunktion J e arvo on pienempi kuin alkuperäisen jaon. Etsi uusi jako sijoittamalla yksi näyte (millainen?) annetun jaon tyhjään joukkoon niin, että kriteerifunktion arvo pienenee. Hint: Given a partition with an empty set, you can always find a partition with smaller criterion value J e by re-placing one sample (what like?) to the empty set. Normi on euklidinen / The norm is Euclidean: y = y T y. Voit soveltaa (todistamatta) tulosta / You may apply (without proving) the result k+ m= x m µ (k+) 2 = k x m µ (k) 2 + k(k + ) µ (k+) µ (k) 2, m= missä / where µ (k) = k k m= x m on keskiarvo laskettuna yli k:n näytteen x m / is the mean computed over k samples x m. 5. Seuraavat neljä opetusnäytettä kahdesta luokasta ω ja ω 2 eivät ole lineaarisesti separoituvia. Havainnollista perceptron-algoritmin tyypillistä toimintaa tällaisessa luokitustilanteessa. The following four training samples from the classes ω and ω 2 are not linearly separable. Demonstrate the typical behavior of the perceptron algorithm in this kind of classification task. 3
11 ω : (0, 0) T ω 2 : (0, ) T (, ) T (, 0) T Ohje: Laske perceptron-algoritmin kriteerifunktion arvo yllä oleville opetusnäytteille jossakin sopivasti valitussa pisteessä a. Sovella perceptron-algoritmia tästä pisteestä a lähtien niin kauan, kunnes löydät algoritmin jakson eli huomaat, ettei algoritmi suppene. Käytä oppimisnopeutena η =. Muista piirrevektorin jatkaminen ja -:llä kertominen. Instruction: Compute the value of the perceptron criterion function for the above four training samples at some appropriately chosen a. Starting from this point a take steps of the perceptron algorithm with the learning rate η = until you find a cycle, that is, the algorithm does not converge. Remember to augment and normalize the feature vectors. (Perceptron-algoritmin kriteerifunktio / Perceptron criterion function: J p (a) = a T y, missä / where Y(a) = {y a T y < 0}.) y Y(a) 6. Erään kaksidimensioisen luokittimen päätöspinnat muodostavat joukon / A twodimensional classifier has decision boundaries which form the following set {(x, y) R 2 x = y x = y + x = y + 2}. (a) Enintään kuinka monen luokan luokitustehtävä on kyseessä? Perustelu. (2p.) (b) Olkoon tehtävässä (a)-kohdan mukainen enimmäismäärä luokkia. Onko luokitin tällöin välttämättä lineaarinen? Todistus. (2p.) (c) Olkoon tehtävässä yksi luokka vähemmän kuin (a)-kohdan enimmäismäärä. Onko luokitin tällöin välttämättä lineaarinen? Todistus. (2p.) (a) At most how many classes does the classification task consist of? Explain. (2p.) (b) Suppose the maximum number of classes, say n. Hence, is the classifier necessarily linear? Proof. (2p.) (c) Now, let the task consist of n classes, that is, one less than the maximum number of classes. Is the classifier here necessarily linear? Proof. (2p.) 4
Capacity Utilization
 Capacity Utilization Tim Schöneberg 28th November Agenda Introduction Fixed and variable input ressources Technical capacity utilization Price based capacity utilization measure Long run and short run
Capacity Utilization Tim Schöneberg 28th November Agenda Introduction Fixed and variable input ressources Technical capacity utilization Price based capacity utilization measure Long run and short run
The CCR Model and Production Correspondence
 The CCR Model and Production Correspondence Tim Schöneberg The 19th of September Agenda Introduction Definitions Production Possiblity Set CCR Model and the Dual Problem Input excesses and output shortfalls
The CCR Model and Production Correspondence Tim Schöneberg The 19th of September Agenda Introduction Definitions Production Possiblity Set CCR Model and the Dual Problem Input excesses and output shortfalls
Bounds on non-surjective cellular automata
 Bounds on non-surjective cellular automata Jarkko Kari Pascal Vanier Thomas Zeume University of Turku LIF Marseille Universität Hannover 27 august 2009 J. Kari, P. Vanier, T. Zeume (UTU) Bounds on non-surjective
Bounds on non-surjective cellular automata Jarkko Kari Pascal Vanier Thomas Zeume University of Turku LIF Marseille Universität Hannover 27 august 2009 J. Kari, P. Vanier, T. Zeume (UTU) Bounds on non-surjective
Returns to Scale II. S ysteemianalyysin. Laboratorio. Esitelmä 8 Timo Salminen. Teknillinen korkeakoulu
 Returns to Scale II Contents Most Productive Scale Size Further Considerations Relaxation of the Convexity Condition Useful Reminder Theorem 5.5 A DMU found to be efficient with a CCR model will also be
Returns to Scale II Contents Most Productive Scale Size Further Considerations Relaxation of the Convexity Condition Useful Reminder Theorem 5.5 A DMU found to be efficient with a CCR model will also be
16. Allocation Models
 16. Allocation Models Juha Saloheimo 17.1.27 S steemianalsin Optimointiopin seminaari - Sks 27 Content Introduction Overall Efficienc with common prices and costs Cost Efficienc S steemianalsin Revenue
16. Allocation Models Juha Saloheimo 17.1.27 S steemianalsin Optimointiopin seminaari - Sks 27 Content Introduction Overall Efficienc with common prices and costs Cost Efficienc S steemianalsin Revenue
Efficiency change over time
 Efficiency change over time Heikki Tikanmäki Optimointiopin seminaari 14.11.2007 Contents Introduction (11.1) Window analysis (11.2) Example, application, analysis Malmquist index (11.3) Dealing with panel
Efficiency change over time Heikki Tikanmäki Optimointiopin seminaari 14.11.2007 Contents Introduction (11.1) Window analysis (11.2) Example, application, analysis Malmquist index (11.3) Dealing with panel
The Viking Battle - Part Version: Finnish
 The Viking Battle - Part 1 015 Version: Finnish Tehtävä 1 Olkoon kokonaisluku, ja olkoon A n joukko A n = { n k k Z, 0 k < n}. Selvitä suurin kokonaisluku M n, jota ei voi kirjoittaa yhden tai useamman
The Viking Battle - Part 1 015 Version: Finnish Tehtävä 1 Olkoon kokonaisluku, ja olkoon A n joukko A n = { n k k Z, 0 k < n}. Selvitä suurin kokonaisluku M n, jota ei voi kirjoittaa yhden tai useamman
Kvanttilaskenta - 1. tehtävät
 Kvanttilaskenta -. tehtävät Johannes Verwijnen January 9, 0 edx-tehtävät Vastauksissa on käytetty edx-kurssin materiaalia.. Problem False, sillä 0 0. Problem False, sillä 0 0 0 0. Problem A quantum state
Kvanttilaskenta -. tehtävät Johannes Verwijnen January 9, 0 edx-tehtävät Vastauksissa on käytetty edx-kurssin materiaalia.. Problem False, sillä 0 0. Problem False, sillä 0 0 0 0. Problem A quantum state
1.3 Lohkorakenne muodostetaan käyttämällä a) puolipistettä b) aaltosulkeita c) BEGIN ja END lausekkeita d) sisennystä
 OULUN YLIOPISTO Tietojenkäsittelytieteiden laitos Johdatus ohjelmointiin 811122P (5 op.) 12.12.2005 Ohjelmointikieli on Java. Tentissä saa olla materiaali mukana. Tenttitulokset julkaistaan aikaisintaan
OULUN YLIOPISTO Tietojenkäsittelytieteiden laitos Johdatus ohjelmointiin 811122P (5 op.) 12.12.2005 Ohjelmointikieli on Java. Tentissä saa olla materiaali mukana. Tenttitulokset julkaistaan aikaisintaan
Kvanttilaskenta - 2. tehtävät
 Kvanttilaskenta -. tehtävät Johannes Verwijnen January 8, 05 edx-tehtävät Vastauksissa on käytetty edx-kurssin materiaalia.. Problem The inner product of + and is. Edelleen false, kts. viikon tehtävä 6..
Kvanttilaskenta -. tehtävät Johannes Verwijnen January 8, 05 edx-tehtävät Vastauksissa on käytetty edx-kurssin materiaalia.. Problem The inner product of + and is. Edelleen false, kts. viikon tehtävä 6..
On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31)
 On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31) Juha Kahkonen Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically On instrument costs
On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31) Juha Kahkonen Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically On instrument costs
SGN-2500 Johdatus hahmontunnistukseen 2007 Luennot 4 ja 5
 SGN-2500 Johdatus hahmontunnistukseen 2007 Luennot 4 ja 5 Jussi Tohka jussi.tohka@tut.fi Signaalinkäsittelyn laitos Tampereen teknillinen yliopisto SGN-2500 Johdatus hahmontunnistukseen 2007Luennot 4 ja
SGN-2500 Johdatus hahmontunnistukseen 2007 Luennot 4 ja 5 Jussi Tohka jussi.tohka@tut.fi Signaalinkäsittelyn laitos Tampereen teknillinen yliopisto SGN-2500 Johdatus hahmontunnistukseen 2007Luennot 4 ja
1.3Lohkorakenne muodostetaan käyttämällä a) puolipistettä b) aaltosulkeita c) BEGIN ja END lausekkeita d) sisennystä
 OULUN YLIOPISTO Tietojenkäsittelytieteiden laitos Johdatus ohjelmointiin 81122P (4 ov.) 30.5.2005 Ohjelmointikieli on Java. Tentissä saa olla materiaali mukana. Tenttitulokset julkaistaan aikaisintaan
OULUN YLIOPISTO Tietojenkäsittelytieteiden laitos Johdatus ohjelmointiin 81122P (4 ov.) 30.5.2005 Ohjelmointikieli on Java. Tentissä saa olla materiaali mukana. Tenttitulokset julkaistaan aikaisintaan
T Statistical Natural Language Processing Answers 6 Collocations Version 1.0
 T-61.5020 Statistical Natural Language Processing Answers 6 Collocations Version 1.0 1. Let s start by calculating the results for pair valkoinen, talo manually: Frequency: Bigrams valkoinen, talo occurred
T-61.5020 Statistical Natural Language Processing Answers 6 Collocations Version 1.0 1. Let s start by calculating the results for pair valkoinen, talo manually: Frequency: Bigrams valkoinen, talo occurred
Alternative DEA Models
 Mat-2.4142 Alternative DEA Models 19.9.2007 Table of Contents Banker-Charnes-Cooper Model Additive Model Example Data Home assignment BCC Model (Banker-Charnes-Cooper) production frontiers spanned by convex
Mat-2.4142 Alternative DEA Models 19.9.2007 Table of Contents Banker-Charnes-Cooper Model Additive Model Example Data Home assignment BCC Model (Banker-Charnes-Cooper) production frontiers spanned by convex
Other approaches to restrict multipliers
 Other approaches to restrict multipliers Heikki Tikanmäki Optimointiopin seminaari 10.10.2007 Contents Short revision (6.2) Another Assurance Region Model (6.3) Cone-Ratio Method (6.4) An Application of
Other approaches to restrict multipliers Heikki Tikanmäki Optimointiopin seminaari 10.10.2007 Contents Short revision (6.2) Another Assurance Region Model (6.3) Cone-Ratio Method (6.4) An Application of
x = y x i = y i i = 1, 2; x + y = (x 1 + y 1, x 2 + y 2 ); x y = (x 1 y 1, x 2 + y 2 );
 LINEAARIALGEBRA Harjoituksia/Exercises 2017 1. Olkoon n Z +. Osoita, että (R n, +, ) on lineaariavaruus, kun vektoreiden x = (x 1,..., x n ), y = (y 1,..., y n ) identtisyys, yhteenlasku ja reaaliluvulla
LINEAARIALGEBRA Harjoituksia/Exercises 2017 1. Olkoon n Z +. Osoita, että (R n, +, ) on lineaariavaruus, kun vektoreiden x = (x 1,..., x n ), y = (y 1,..., y n ) identtisyys, yhteenlasku ja reaaliluvulla
HARJOITUS- PAKETTI A
 Logistiikka A35A00310 Tuotantotalouden perusteet HARJOITUS- PAKETTI A (6 pistettä) TUTA 19 Luento 3.Ennustaminen County General 1 piste The number of heart surgeries performed at County General Hospital
Logistiikka A35A00310 Tuotantotalouden perusteet HARJOITUS- PAKETTI A (6 pistettä) TUTA 19 Luento 3.Ennustaminen County General 1 piste The number of heart surgeries performed at County General Hospital
On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31)
 On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31) Juha Kahkonen Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically On instrument costs
On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31) Juha Kahkonen Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically On instrument costs
812336A C++ -kielen perusteet, 21.8.2010
 812336A C++ -kielen perusteet, 21.8.2010 1. Vastaa lyhyesti seuraaviin kysymyksiin (1p kaikista): a) Mitä tarkoittaa funktion ylikuormittaminen (overloading)? b) Mitä tarkoittaa jäsenfunktion ylimääritys
812336A C++ -kielen perusteet, 21.8.2010 1. Vastaa lyhyesti seuraaviin kysymyksiin (1p kaikista): a) Mitä tarkoittaa funktion ylikuormittaminen (overloading)? b) Mitä tarkoittaa jäsenfunktion ylimääritys
anna minun kertoa let me tell you
 anna minun kertoa let me tell you anna minun kertoa I OSA 1. Anna minun kertoa sinulle mitä oli. Tiedän että osaan. Kykenen siihen. Teen nyt niin. Minulla on oikeus. Sanani voivat olla puutteellisia mutta
anna minun kertoa let me tell you anna minun kertoa I OSA 1. Anna minun kertoa sinulle mitä oli. Tiedän että osaan. Kykenen siihen. Teen nyt niin. Minulla on oikeus. Sanani voivat olla puutteellisia mutta
Teknillinen tiedekunta, matematiikan jaos Numeeriset menetelmät
 Numeeriset menetelmät 1. välikoe, 14.2.2009 1. Määrää matriisin 1 1 a 1 3 a a 4 a a 2 1 LU-hajotelma kaikille a R. Ratkaise LU-hajotelmaa käyttäen yhtälöryhmä Ax = b, missä b = [ 1 3 2a 2 a + 3] T. 2.
Numeeriset menetelmät 1. välikoe, 14.2.2009 1. Määrää matriisin 1 1 a 1 3 a a 4 a a 2 1 LU-hajotelma kaikille a R. Ratkaise LU-hajotelmaa käyttäen yhtälöryhmä Ax = b, missä b = [ 1 3 2a 2 a + 3] T. 2.
RINNAKKAINEN OHJELMOINTI A,
 RINNAKKAINEN OHJELMOINTI 815301A, 18.6.2005 1. Vastaa lyhyesti (2p kustakin): a) Mitkä ovat rinnakkaisen ohjelman oikeellisuuskriteerit? b) Mitä tarkoittaa laiska säikeen luominen? c) Mitä ovat kohtaaminen
RINNAKKAINEN OHJELMOINTI 815301A, 18.6.2005 1. Vastaa lyhyesti (2p kustakin): a) Mitkä ovat rinnakkaisen ohjelman oikeellisuuskriteerit? b) Mitä tarkoittaa laiska säikeen luominen? c) Mitä ovat kohtaaminen
Topologies on pseudoinnite paths
 Topologies on pseudoinnite paths Andrey Kudinov Institute for Information Transmission Problems, Moscow National Research University Higher School of Economics, Moscow Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology
Topologies on pseudoinnite paths Andrey Kudinov Institute for Information Transmission Problems, Moscow National Research University Higher School of Economics, Moscow Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology
Gap-filling methods for CH 4 data
 Gap-filling methods for CH 4 data Sigrid Dengel University of Helsinki Outline - Ecosystems known for CH 4 emissions; - Why is gap-filling of CH 4 data not as easy and straight forward as CO 2 ; - Gap-filling
Gap-filling methods for CH 4 data Sigrid Dengel University of Helsinki Outline - Ecosystems known for CH 4 emissions; - Why is gap-filling of CH 4 data not as easy and straight forward as CO 2 ; - Gap-filling
Toppila/Kivistö 10.01.2013 Vastaa kaikkin neljään tehtävään, jotka kukin arvostellaan asteikolla 0-6 pistettä.
 ..23 Vastaa kaikkin neljään tehtävään, jotka kukin arvostellaan asteikolla -6 pistettä. Tehtävä Ovatko seuraavat väittämät oikein vai väärin? Perustele vastauksesi. (a) Lineaarisen kokonaislukutehtävän
..23 Vastaa kaikkin neljään tehtävään, jotka kukin arvostellaan asteikolla -6 pistettä. Tehtävä Ovatko seuraavat väittämät oikein vai väärin? Perustele vastauksesi. (a) Lineaarisen kokonaislukutehtävän
Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 4, viikko 40
 Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 4, viikko 40 H4t1, Exercise 4.2. H4t2, Exercise 4.3. H4t3, Exercise 4.4. H4t4, Exercise 4.5. H4t5, Exercise 4.6. (Exercise 4.2.) 1 4.2. Solve the LP max z = x 1 + 2x 2
Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 4, viikko 40 H4t1, Exercise 4.2. H4t2, Exercise 4.3. H4t3, Exercise 4.4. H4t4, Exercise 4.5. H4t5, Exercise 4.6. (Exercise 4.2.) 1 4.2. Solve the LP max z = x 1 + 2x 2
S-55.1100 SÄHKÖTEKNIIKKA JA ELEKTRONIIKKA
 S-55.00 SÄHKÖKNKKA A KONKKA. välikoe 2..2008. Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään!. aske jännite U. = 4 Ω, 2 = Ω, = Ω, = 2, 2 =, = A, 2 = U 2 2 2 2. ännitelähde tuottaa hetkestä t = t < 0 alkaen kaksiportaisen
S-55.00 SÄHKÖKNKKA A KONKKA. välikoe 2..2008. Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään!. aske jännite U. = 4 Ω, 2 = Ω, = Ω, = 2, 2 =, = A, 2 = U 2 2 2 2. ännitelähde tuottaa hetkestä t = t < 0 alkaen kaksiportaisen
1. SIT. The handler and dog stop with the dog sitting at heel. When the dog is sitting, the handler cues the dog to heel forward.
 START START SIT 1. SIT. The handler and dog stop with the dog sitting at heel. When the dog is sitting, the handler cues the dog to heel forward. This is a static exercise. SIT STAND 2. SIT STAND. The
START START SIT 1. SIT. The handler and dog stop with the dog sitting at heel. When the dog is sitting, the handler cues the dog to heel forward. This is a static exercise. SIT STAND 2. SIT STAND. The
Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 2, viikko 38
 Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 2, viikko 38 H2t1, Exercise 1.1. H2t2, Exercise 1.2. H2t3, Exercise 2.3. H2t4, Exercise 2.4. H2t5, Exercise 2.5. (Exercise 1.1.) 1 1.1. Model the following problem mathematically:
Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 2, viikko 38 H2t1, Exercise 1.1. H2t2, Exercise 1.2. H2t3, Exercise 2.3. H2t4, Exercise 2.4. H2t5, Exercise 2.5. (Exercise 1.1.) 1 1.1. Model the following problem mathematically:
Results on the new polydrug use questions in the Finnish TDI data
 Results on the new polydrug use questions in the Finnish TDI data Multi-drug use, polydrug use and problematic polydrug use Martta Forsell, Finnish Focal Point 28/09/2015 Martta Forsell 1 28/09/2015 Esityksen
Results on the new polydrug use questions in the Finnish TDI data Multi-drug use, polydrug use and problematic polydrug use Martta Forsell, Finnish Focal Point 28/09/2015 Martta Forsell 1 28/09/2015 Esityksen
Information on preparing Presentation
 Information on preparing Presentation Seminar on big data management Lecturer: Spring 2017 20.1.2017 1 Agenda Hints and tips on giving a good presentation Watch two videos and discussion 22.1.2017 2 Goals
Information on preparing Presentation Seminar on big data management Lecturer: Spring 2017 20.1.2017 1 Agenda Hints and tips on giving a good presentation Watch two videos and discussion 22.1.2017 2 Goals
C++11 seminaari, kevät Johannes Koskinen
 C++11 seminaari, kevät 2012 Johannes Koskinen Sisältö Mikä onkaan ongelma? Standardidraftin luku 29: Atomiset tyypit Muistimalli Rinnakkaisuus On multicore systems, when a thread writes a value to memory,
C++11 seminaari, kevät 2012 Johannes Koskinen Sisältö Mikä onkaan ongelma? Standardidraftin luku 29: Atomiset tyypit Muistimalli Rinnakkaisuus On multicore systems, when a thread writes a value to memory,
Uusi Ajatus Löytyy Luonnosta 4 (käsikirja) (Finnish Edition)
 Uusi Ajatus Löytyy Luonnosta 4 (käsikirja) (Finnish Edition) Esko Jalkanen Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Uusi Ajatus Löytyy Luonnosta 4 (käsikirja) (Finnish Edition) Esko Jalkanen
Uusi Ajatus Löytyy Luonnosta 4 (käsikirja) (Finnish Edition) Esko Jalkanen Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Uusi Ajatus Löytyy Luonnosta 4 (käsikirja) (Finnish Edition) Esko Jalkanen
On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31)
 On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31) Juha Kahkonen Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically On instrument costs
On instrument costs in decentralized macroeconomic decision making (Helsingin Kauppakorkeakoulun julkaisuja ; D-31) Juha Kahkonen Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically On instrument costs
S SÄHKÖTEKNIIKKA JA ELEKTRONIIKKA
 S-55.1100 SÄHKÖTKNIIKKA JA LKTONIIKKA Tentti 15.5.2006: tehtävät 1,3,5,7,10 1. välikoe: tehtävät 1,2,3,4,5 2. välikoe: tehtävät 6,7,8,9,10 Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään/koe; ne sinun pitää itse valita!
S-55.1100 SÄHKÖTKNIIKKA JA LKTONIIKKA Tentti 15.5.2006: tehtävät 1,3,5,7,10 1. välikoe: tehtävät 1,2,3,4,5 2. välikoe: tehtävät 6,7,8,9,10 Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään/koe; ne sinun pitää itse valita!
Network to Get Work. Tehtäviä opiskelijoille Assignments for students. www.laurea.fi
 Network to Get Work Tehtäviä opiskelijoille Assignments for students www.laurea.fi Ohje henkilöstölle Instructions for Staff Seuraavassa on esitetty joukko tehtäviä, joista voit valita opiskelijaryhmällesi
Network to Get Work Tehtäviä opiskelijoille Assignments for students www.laurea.fi Ohje henkilöstölle Instructions for Staff Seuraavassa on esitetty joukko tehtäviä, joista voit valita opiskelijaryhmällesi
Counting quantities 1-3
 Counting quantities 1-3 Lukumäärien 1 3 laskeminen 1. Rastita Tick (X) (X) the kummassa box that has laatikossa more on balls enemmän in it. palloja. X. Rastita Tick (X) (X) the kummassa box that has laatikossa
Counting quantities 1-3 Lukumäärien 1 3 laskeminen 1. Rastita Tick (X) (X) the kummassa box that has laatikossa more on balls enemmän in it. palloja. X. Rastita Tick (X) (X) the kummassa box that has laatikossa
Capacity utilization
 Mat-2.4142 Seminar on optimization Capacity utilization 12.12.2007 Contents Summary of chapter 14 Related DEA-solver models Illustrative examples Measure of technical capacity utilization Price-based measure
Mat-2.4142 Seminar on optimization Capacity utilization 12.12.2007 Contents Summary of chapter 14 Related DEA-solver models Illustrative examples Measure of technical capacity utilization Price-based measure
FinFamily PostgreSQL installation ( ) FinFamily PostgreSQL
 FinFamily PostgreSQL 1 Sisällys / Contents FinFamily PostgreSQL... 1 1. Asenna PostgreSQL tietokanta / Install PostgreSQL database... 3 1.1. PostgreSQL tietokannasta / About the PostgreSQL database...
FinFamily PostgreSQL 1 Sisällys / Contents FinFamily PostgreSQL... 1 1. Asenna PostgreSQL tietokanta / Install PostgreSQL database... 3 1.1. PostgreSQL tietokannasta / About the PostgreSQL database...
Ajettavat luokat: SM: S1 (25 aika-ajon nopeinta)
 SUPERMOTO SM 2013 OULU Lisämääräys ja ohje Oulun Moottorikerho ry ja Oulun Formula K-125ry toivottaa SuperMoto kuljettajat osallistumaan SuperMoto SM 2013 Oulu osakilpailuun. Kilpailu ajetaan karting radalla
SUPERMOTO SM 2013 OULU Lisämääräys ja ohje Oulun Moottorikerho ry ja Oulun Formula K-125ry toivottaa SuperMoto kuljettajat osallistumaan SuperMoto SM 2013 Oulu osakilpailuun. Kilpailu ajetaan karting radalla
Statistical design. Tuomas Selander
 Statistical design Tuomas Selander 28.8.2014 Introduction Biostatistician Work area KYS-erva KYS, Jyväskylä, Joensuu, Mikkeli, Savonlinna Work tasks Statistical methods, selection and quiding Data analysis
Statistical design Tuomas Selander 28.8.2014 Introduction Biostatistician Work area KYS-erva KYS, Jyväskylä, Joensuu, Mikkeli, Savonlinna Work tasks Statistical methods, selection and quiding Data analysis
Huom. tämä kulma on yhtä suuri kuin ohjauskulman muutos. lasketaan ajoneuvon keskipisteen ympyräkaaren jänteen pituus
 AS-84.327 Paikannus- ja navigointimenetelmät Ratkaisut 2.. a) Kun kuvan ajoneuvon kumpaakin pyörää pyöritetään tasaisella nopeudella, ajoneuvon rata on ympyränkaaren segmentin muotoinen. Hitaammin kulkeva
AS-84.327 Paikannus- ja navigointimenetelmät Ratkaisut 2.. a) Kun kuvan ajoneuvon kumpaakin pyörää pyöritetään tasaisella nopeudella, ajoneuvon rata on ympyränkaaren segmentin muotoinen. Hitaammin kulkeva
WindPRO version joulu 2012 Printed/Page :47 / 1. SHADOW - Main Result
 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.8.579
SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.8.579
TM ETRS-TM35FIN-ETRS89 WTG
 SHADOW - Main Result Calculation: N117 x 9 x HH141 Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG
SHADOW - Main Result Calculation: N117 x 9 x HH141 Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG
S SÄHKÖTEKNIIKKA JA ELEKTRONIIKKA
 S-55.00 SÄHKÖTKNKKA JA LKTONKKA. välikoe 3.0.2006. Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään!. Laske jännite U. = =4Ω, 3 =2Ω, = =2V, J =2A, J 2 =3A + J 2 + J 3 2. Kondensaattori on aluksi varautunut jännitteeseen
S-55.00 SÄHKÖTKNKKA JA LKTONKKA. välikoe 3.0.2006. Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään!. Laske jännite U. = =4Ω, 3 =2Ω, = =2V, J =2A, J 2 =3A + J 2 + J 3 2. Kondensaattori on aluksi varautunut jännitteeseen
E80. Data Uncertainty, Data Fitting, Error Propagation. Jan. 23, 2014 Jon Roberts. Experimental Engineering
 Lecture 2 Data Uncertainty, Data Fitting, Error Propagation Jan. 23, 2014 Jon Roberts Purpose & Outline Data Uncertainty & Confidence in Measurements Data Fitting - Linear Regression Error Propagation
Lecture 2 Data Uncertainty, Data Fitting, Error Propagation Jan. 23, 2014 Jon Roberts Purpose & Outline Data Uncertainty & Confidence in Measurements Data Fitting - Linear Regression Error Propagation
WindPRO version joulu 2012 Printed/Page :42 / 1. SHADOW - Main Result
 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table 13.6.2013 19:42 / 1 Minimum
SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table 13.6.2013 19:42 / 1 Minimum
SIMULINK S-funktiot. SIMULINK S-funktiot
 S-funktio on ohjelmointikielellä (Matlab, C, Fortran) laadittu oma algoritmi tai dynaamisen järjestelmän kuvaus, jota voidaan käyttää Simulink-malleissa kuin mitä tahansa valmista lohkoa. S-funktion rakenne
S-funktio on ohjelmointikielellä (Matlab, C, Fortran) laadittu oma algoritmi tai dynaamisen järjestelmän kuvaus, jota voidaan käyttää Simulink-malleissa kuin mitä tahansa valmista lohkoa. S-funktion rakenne
Choose Finland-Helsinki Valitse Finland-Helsinki
 Write down the Temporary Application ID. If you do not manage to complete the form you can continue where you stopped with this ID no. Muista Temporary Application ID. Jos et onnistu täyttää lomake loppuun
Write down the Temporary Application ID. If you do not manage to complete the form you can continue where you stopped with this ID no. Muista Temporary Application ID. Jos et onnistu täyttää lomake loppuun
FinFamily Installation and importing data (11.1.2016) FinFamily Asennus / Installation
 FinFamily Asennus / Installation 1 Sisällys / Contents FinFamily Asennus / Installation... 1 1. Asennus ja tietojen tuonti / Installation and importing data... 4 1.1. Asenna Java / Install Java... 4 1.2.
FinFamily Asennus / Installation 1 Sisällys / Contents FinFamily Asennus / Installation... 1 1. Asennus ja tietojen tuonti / Installation and importing data... 4 1.1. Asenna Java / Install Java... 4 1.2.
TM ETRS-TM35FIN-ETRS89 WTG
 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.8.579
SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.8.579
,0 Yes ,0 120, ,8
 SHADOW - Main Result Calculation: Alue 2 ( x 9 x HH120) TuuliSaimaa kaavaluonnos Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered
SHADOW - Main Result Calculation: Alue 2 ( x 9 x HH120) TuuliSaimaa kaavaluonnos Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered
( ,5 1 1,5 2 km
 Tuulivoimala Rakennukset Asuinrakennus Liikerak. tai Julkinen rak. Lomarakennus Teollinen rakennus Kirkollinen rakennus Varjostus "real case" h/a 1 h/a 8 h/a 20 h/a 4 5 3 1 2 6 7 8 9 10 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 km
Tuulivoimala Rakennukset Asuinrakennus Liikerak. tai Julkinen rak. Lomarakennus Teollinen rakennus Kirkollinen rakennus Varjostus "real case" h/a 1 h/a 8 h/a 20 h/a 4 5 3 1 2 6 7 8 9 10 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 km
TM ETRS-TM35FIN-ETRS89 WTG
 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table 5.11.2013 16:44 / 1 Minimum
SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table 5.11.2013 16:44 / 1 Minimum
Guidebook for Multicultural TUT Users
 1 Guidebook for Multicultural TUT Users WORKPLACE PIRKANMAA-hankkeen KESKUSTELUTILAISUUS 16.12.2010 Hyvää käytäntöä kehittämässä - vuorovaikutusopas kansainvälisille opiskelijoille TTY Teknis-taloudellinen
1 Guidebook for Multicultural TUT Users WORKPLACE PIRKANMAA-hankkeen KESKUSTELUTILAISUUS 16.12.2010 Hyvää käytäntöä kehittämässä - vuorovaikutusopas kansainvälisille opiskelijoille TTY Teknis-taloudellinen
Counting quantities 1-3
 Counting quantities 1-3 Lukumäärien 1 3 laskeminen 1. Rastita Tick (X) (X) the kummassa box that has laatikossa more on balls enemmän in it. palloja. X 2. Rastita Tick (X) (X) the kummassa box that has
Counting quantities 1-3 Lukumäärien 1 3 laskeminen 1. Rastita Tick (X) (X) the kummassa box that has laatikossa more on balls enemmän in it. palloja. X 2. Rastita Tick (X) (X) the kummassa box that has
TM ETRS-TM35FIN-ETRS89 WTG
 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table 22.12.2014 11:33 / 1 Minimum
SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table 22.12.2014 11:33 / 1 Minimum
make and make and make ThinkMath 2017
 Adding quantities Lukumäärienup yhdistäminen. Laske yhteensä?. Countkuinka howmonta manypalloja ballson there are altogether. and ja make and make and ja make on and ja make ThinkMath 7 on ja on on Vaihdannaisuus
Adding quantities Lukumäärienup yhdistäminen. Laske yhteensä?. Countkuinka howmonta manypalloja ballson there are altogether. and ja make and make and ja make on and ja make ThinkMath 7 on ja on on Vaihdannaisuus
Metsälamminkankaan tuulivoimapuiston osayleiskaava
 VAALAN KUNTA TUULISAIMAA OY Metsälamminkankaan tuulivoimapuiston osayleiskaava Liite 3. Varjostusmallinnus FCG SUUNNITTELU JA TEKNIIKKA OY 12.5.2015 P25370 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations
VAALAN KUNTA TUULISAIMAA OY Metsälamminkankaan tuulivoimapuiston osayleiskaava Liite 3. Varjostusmallinnus FCG SUUNNITTELU JA TEKNIIKKA OY 12.5.2015 P25370 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations
AYYE 9/ HOUSING POLICY
 AYYE 9/12 2.10.2012 HOUSING POLICY Mission for AYY Housing? What do we want to achieve by renting apartments? 1) How many apartments do we need? 2) What kind of apartments do we need? 3) To whom do we
AYYE 9/12 2.10.2012 HOUSING POLICY Mission for AYY Housing? What do we want to achieve by renting apartments? 1) How many apartments do we need? 2) What kind of apartments do we need? 3) To whom do we
Laskennallisesti Älykkäät Järjestelmät. Sumean kmeans ja kmeans algoritmien vertailu
 Laskennallisesti Älykkäät Järjestelmät Sumean kmeans ja kmeans algoritmien vertailu Annemari Auvinen (annauvi@st.jyu.fi) Anu Niemi (anniemi@st.jyu.fi) 28.5.2002 1 Tehtävän kuvaus Tehtävänämme oli verrata
Laskennallisesti Älykkäät Järjestelmät Sumean kmeans ja kmeans algoritmien vertailu Annemari Auvinen (annauvi@st.jyu.fi) Anu Niemi (anniemi@st.jyu.fi) 28.5.2002 1 Tehtävän kuvaus Tehtävänämme oli verrata
Exercise 1. (session: )
 EEN-E3001, FUNDAMENTALS IN INDUSTRIAL ENERGY ENGINEERING Exercise 1 (session: 24.1.2017) Problem 3 will be graded. The deadline for the return is on 31.1. at 12:00 am (before the exercise session). You
EEN-E3001, FUNDAMENTALS IN INDUSTRIAL ENERGY ENGINEERING Exercise 1 (session: 24.1.2017) Problem 3 will be graded. The deadline for the return is on 31.1. at 12:00 am (before the exercise session). You
S Sähkön jakelu ja markkinat S Electricity Distribution and Markets
 S-18.3153 Sähkön jakelu ja markkinat S-18.3154 Electricity Distribution and Markets Voltage Sag 1) Kolmivaiheinen vastukseton oikosulku tapahtuu 20 kv lähdöllä etäisyydellä 1 km, 3 km, 5 km, 8 km, 10 km
S-18.3153 Sähkön jakelu ja markkinat S-18.3154 Electricity Distribution and Markets Voltage Sag 1) Kolmivaiheinen vastukseton oikosulku tapahtuu 20 kv lähdöllä etäisyydellä 1 km, 3 km, 5 km, 8 km, 10 km
LYTH-CONS CONSISTENCY TRANSMITTER
 LYTH-CONS CONSISTENCY TRANSMITTER LYTH-INSTRUMENT OY has generate new consistency transmitter with blade-system to meet high technical requirements in Pulp&Paper industries. Insurmountable advantages are
LYTH-CONS CONSISTENCY TRANSMITTER LYTH-INSTRUMENT OY has generate new consistency transmitter with blade-system to meet high technical requirements in Pulp&Paper industries. Insurmountable advantages are
1. Liikkuvat määreet
 1. Liikkuvat määreet Väitelauseen perussanajärjestys: SPOTPA (subj. + pred. + obj. + tapa + paikka + aika) Suora sanajärjestys = subjekti on ennen predikaattia tekijä tekeminen Alasääntö 1: Liikkuvat määreet
1. Liikkuvat määreet Väitelauseen perussanajärjestys: SPOTPA (subj. + pred. + obj. + tapa + paikka + aika) Suora sanajärjestys = subjekti on ennen predikaattia tekijä tekeminen Alasääntö 1: Liikkuvat määreet
Valuation of Asian Quanto- Basket Options
 Valuation of Asian Quanto- Basket Options (Final Presentation) 21.11.2011 Thesis Instructor and Supervisor: Prof. Ahti Salo Työn saa tallentaa ja julkistaa Aalto-yliopiston avoimilla verkkosivuilla. Muilta
Valuation of Asian Quanto- Basket Options (Final Presentation) 21.11.2011 Thesis Instructor and Supervisor: Prof. Ahti Salo Työn saa tallentaa ja julkistaa Aalto-yliopiston avoimilla verkkosivuilla. Muilta
7.4 Variability management
 7.4 Variability management time... space software product-line should support variability in space (different products) support variability in time (maintenance, evolution) 1 Product variation Product
7.4 Variability management time... space software product-line should support variability in space (different products) support variability in time (maintenance, evolution) 1 Product variation Product
Returns to Scale Chapters
 Return to Scale Chapter 5.1-5.4 Saara Tuurala 26.9.2007 Index Introduction Baic Formulation of Retur to Scale Geometric Portrayal in DEA BCC Return to Scale CCR Return to Scale Summary Home Aignment Introduction
Return to Scale Chapter 5.1-5.4 Saara Tuurala 26.9.2007 Index Introduction Baic Formulation of Retur to Scale Geometric Portrayal in DEA BCC Return to Scale CCR Return to Scale Summary Home Aignment Introduction
Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 3, viikko 39
 Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 3, viikko 39 H3t1, Exercise 3.1. H3t2, Exercise 3.2. H3t3, Exercise 3.3. H3t4, Exercise 3.4. H3t5 (Exercise 3.1.) 1 3.1. Find the (a) standard form, (b) slack form of the
Operatioanalyysi 2011, Harjoitus 3, viikko 39 H3t1, Exercise 3.1. H3t2, Exercise 3.2. H3t3, Exercise 3.3. H3t4, Exercise 3.4. H3t5 (Exercise 3.1.) 1 3.1. Find the (a) standard form, (b) slack form of the
Harha mallin arvioinnissa
 Esitelmä 12 Antti Toppila sivu 1/18 Optimointiopin seminaari Syksy 2010 Harha mallin arvioinnissa Antti Toppila 13.10.2010 Esitelmä 12 Antti Toppila sivu 2/18 Optimointiopin seminaari Syksy 2010 Sisältö
Esitelmä 12 Antti Toppila sivu 1/18 Optimointiopin seminaari Syksy 2010 Harha mallin arvioinnissa Antti Toppila 13.10.2010 Esitelmä 12 Antti Toppila sivu 2/18 Optimointiopin seminaari Syksy 2010 Sisältö
Ohjelmointikielet ja -paradigmat 5op. Markus Norrena
 Ohjelmointikielet ja -paradigmat 5op Markus Norrena Kotitehtävä 6, toteuttakaa alla olevan luokka ja attribuutit (muuttujat) Kotitehtävä 6, toteuttakaa alla olevan luokka ja attribuutit (muuttujat) Huom!
Ohjelmointikielet ja -paradigmat 5op Markus Norrena Kotitehtävä 6, toteuttakaa alla olevan luokka ja attribuutit (muuttujat) Kotitehtävä 6, toteuttakaa alla olevan luokka ja attribuutit (muuttujat) Huom!
( ( OX2 Perkkiö. Rakennuskanta. Varjostus. 9 x N131 x HH145
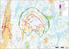 OX2 9 x N131 x HH145 Rakennuskanta Asuinrakennus Lomarakennus Liike- tai julkinen rakennus Teollinen rakennus Kirkko tai kirkollinen rak. Muu rakennus Allas Varjostus 1 h/a 8 h/a 20 h/a 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 km
OX2 9 x N131 x HH145 Rakennuskanta Asuinrakennus Lomarakennus Liike- tai julkinen rakennus Teollinen rakennus Kirkko tai kirkollinen rak. Muu rakennus Allas Varjostus 1 h/a 8 h/a 20 h/a 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 km
Travel Getting Around
 - Location Olen eksyksissä. Not knowing where you are Voisitko näyttää kartalta missä sen on? Asking for a specific location on a map Mistä täällä on? Asking for a specific...wc?...pankki / rahanvaihtopiste?...hotelli?...huoltoasema?...sairaala?...apteekki?...tavaratalo?...ruokakauppa?...bussipysäkki?
- Location Olen eksyksissä. Not knowing where you are Voisitko näyttää kartalta missä sen on? Asking for a specific location on a map Mistä täällä on? Asking for a specific...wc?...pankki / rahanvaihtopiste?...hotelli?...huoltoasema?...sairaala?...apteekki?...tavaratalo?...ruokakauppa?...bussipysäkki?
Telecommunication Software
 Telecommunication Software Final exam 21.11.2006 COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORY 521265A Vastaukset englanniksi tai suomeksi. / Answers in English or in Finnish. 1. (a) Määrittele sovellusviesti, PersonnelRecord,
Telecommunication Software Final exam 21.11.2006 COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORY 521265A Vastaukset englanniksi tai suomeksi. / Answers in English or in Finnish. 1. (a) Määrittele sovellusviesti, PersonnelRecord,
Tynnyrivaara, OX2 Tuulivoimahanke. ( Layout 9 x N131 x HH145. Rakennukset Asuinrakennus Lomarakennus 9 x N131 x HH145 Varjostus 1 h/a 8 h/a 20 h/a
 , Tuulivoimahanke Layout 9 x N131 x HH145 Rakennukset Asuinrakennus Lomarakennus 9 x N131 x HH145 Varjostus 1 h/a 8 h/a 20 h/a 0 0,5 1 1,5 km 2 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations
, Tuulivoimahanke Layout 9 x N131 x HH145 Rakennukset Asuinrakennus Lomarakennus 9 x N131 x HH145 Varjostus 1 h/a 8 h/a 20 h/a 0 0,5 1 1,5 km 2 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations
FIS IMATRAN KYLPYLÄHIIHDOT Team captains meeting
 FIS IMATRAN KYLPYLÄHIIHDOT 8.-9.12.2018 Team captains meeting 8.12.2018 Agenda 1 Opening of the meeting 2 Presence 3 Organizer s personell 4 Jury 5 Weather forecast 6 Composition of competitors startlists
FIS IMATRAN KYLPYLÄHIIHDOT 8.-9.12.2018 Team captains meeting 8.12.2018 Agenda 1 Opening of the meeting 2 Presence 3 Organizer s personell 4 Jury 5 Weather forecast 6 Composition of competitors startlists
A DEA Game II. Juha Saloheimo S ysteemianalyysin. Laboratorio. Teknillinen korkeakoulu
 A DEA Game II Juha Salohemo 12.12.2007 Content Recap of the Example The Shapley Value Margnal Contrbuton, Ordered Coaltons, Soluton to the Example DEA Mn Game Summary Home Assgnment Recap of the Example
A DEA Game II Juha Salohemo 12.12.2007 Content Recap of the Example The Shapley Value Margnal Contrbuton, Ordered Coaltons, Soluton to the Example DEA Mn Game Summary Home Assgnment Recap of the Example
S SÄHKÖTEKNIIKKA JA ELEKTRONIIKKA
 S-55.1100 SÄHKÖTKNIIKKA JA LKTONIIKKA 2. välikoe 14.12.2010. Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään! Sallitut: Kako, (gr.) laskin, [MAOL], [sanakirjan käytöstä sovittava valvojan kanssa!] 1. Missä rajoissa
S-55.1100 SÄHKÖTKNIIKKA JA LKTONIIKKA 2. välikoe 14.12.2010. Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään! Sallitut: Kako, (gr.) laskin, [MAOL], [sanakirjan käytöstä sovittava valvojan kanssa!] 1. Missä rajoissa
VAASAN YLIOPISTO Humanististen tieteiden kandidaatin tutkinto / Filosofian maisterin tutkinto
 VAASAN YLIOPISTO Humanististen tieteiden kandidaatin tutkinto / Filosofian maisterin tutkinto Tämän viestinnän, nykysuomen ja englannin kandidaattiohjelman valintakokeen avulla Arvioidaan viestintävalmiuksia,
VAASAN YLIOPISTO Humanististen tieteiden kandidaatin tutkinto / Filosofian maisterin tutkinto Tämän viestinnän, nykysuomen ja englannin kandidaattiohjelman valintakokeen avulla Arvioidaan viestintävalmiuksia,
TM ETRS-TM35FIN-ETRS89 WTG
 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.8.579
SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.8.579
TM ETRS-TM35FIN-ETRS89 WTG
 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.8.579
SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.8.579
National Building Code of Finland, Part D1, Building Water Supply and Sewerage Systems, Regulations and guidelines 2007
 National Building Code of Finland, Part D1, Building Water Supply and Sewerage Systems, Regulations and guidelines 2007 Chapter 2.4 Jukka Räisä 1 WATER PIPES PLACEMENT 2.4.1 Regulation Water pipe and its
National Building Code of Finland, Part D1, Building Water Supply and Sewerage Systems, Regulations and guidelines 2007 Chapter 2.4 Jukka Räisä 1 WATER PIPES PLACEMENT 2.4.1 Regulation Water pipe and its
Increase of opioid use in Finland when is there enough key indicator data to state a trend?
 Increase of opioid use in Finland when is there enough key indicator data to state a trend? Martta Forsell, Finnish Focal Point 28.9.2015 Esityksen nimi / Tekijä 1 Martta Forsell Master of Social Sciences
Increase of opioid use in Finland when is there enough key indicator data to state a trend? Martta Forsell, Finnish Focal Point 28.9.2015 Esityksen nimi / Tekijä 1 Martta Forsell Master of Social Sciences
Alternatives to the DFT
 Alternatives to the DFT Doru Balcan Carnegie Mellon University joint work with Aliaksei Sandryhaila, Jonathan Gross, and Markus Püschel - appeared in IEEE ICASSP 08 - Introduction Discrete time signal
Alternatives to the DFT Doru Balcan Carnegie Mellon University joint work with Aliaksei Sandryhaila, Jonathan Gross, and Markus Püschel - appeared in IEEE ICASSP 08 - Introduction Discrete time signal
TM ETRS-TM35FIN-ETRS89 WTG
 SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.9.269
SHADOW - Main Result Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please look in WTG table WindPRO version 2.9.269
800323A KUNTALAAJENNUKSET OSA II FIELD EXTENSIONS PART II
 800323A KUNTALAAJENNUKSET OSA II FIELD EXTENSIONS PART II Tapani Matala-aho MATEMATIIKKA/LUTK/OULUN YLIOPISTO KEVÄT 2018 Tapani Matala-aho MATEMATIIKKA/LUTK/OULUN 800323A KUNTALAAJENNUKSET YLIOPISTO OSA
800323A KUNTALAAJENNUKSET OSA II FIELD EXTENSIONS PART II Tapani Matala-aho MATEMATIIKKA/LUTK/OULUN YLIOPISTO KEVÄT 2018 Tapani Matala-aho MATEMATIIKKA/LUTK/OULUN 800323A KUNTALAAJENNUKSET YLIOPISTO OSA
I. AES Rijndael. Rijndael - Internal Structure
 I. AES Rndael NOKIA T-79.53 Additional material Oct 3/KN Rndael - Internal Structure Rndael is an iterated block cipher with variable length block and variable key size. The number of rounds is defined
I. AES Rndael NOKIA T-79.53 Additional material Oct 3/KN Rndael - Internal Structure Rndael is an iterated block cipher with variable length block and variable key size. The number of rounds is defined
Constructive Alignment in Specialisation Studies in Industrial Pharmacy in Finland
 Constructive Alignment in Specialisation Studies in Industrial Pharmacy in Finland Anne Mari Juppo, Nina Katajavuori University of Helsinki Faculty of Pharmacy 23.7.2012 1 Background Pedagogic research
Constructive Alignment in Specialisation Studies in Industrial Pharmacy in Finland Anne Mari Juppo, Nina Katajavuori University of Helsinki Faculty of Pharmacy 23.7.2012 1 Background Pedagogic research
21~--~--~r--1~~--~--~~r--1~
 - K.Loberg FYSE420 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS 13.05.2011 1. Toteuta alla esitetyn sekvenssin tuottava asynkroninen pun. Anna heratefunktiot, siirtotaulukko ja kokonaistilataulukko ( exitation functions, transition
- K.Loberg FYSE420 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS 13.05.2011 1. Toteuta alla esitetyn sekvenssin tuottava asynkroninen pun. Anna heratefunktiot, siirtotaulukko ja kokonaistilataulukko ( exitation functions, transition
TM ETRS-TM35FIN-ETRS89 WTG
 VE1 SHADOW - Main Result Calculation: 8 x Nordex N131 x HH145m Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please
VE1 SHADOW - Main Result Calculation: 8 x Nordex N131 x HH145m Assumptions for shadow calculations Maximum distance for influence Calculate only when more than 20 % of sun is covered by the blade Please
Rekisteröiminen - FAQ
 Rekisteröiminen - FAQ Miten Akun/laturin rekisteröiminen tehdään Akun/laturin rekisteröiminen tapahtuu samalla tavalla kuin nykyinen takuurekisteröityminen koneille. Nykyistä tietokantaa on muokattu niin,
Rekisteröiminen - FAQ Miten Akun/laturin rekisteröiminen tehdään Akun/laturin rekisteröiminen tapahtuu samalla tavalla kuin nykyinen takuurekisteröityminen koneille. Nykyistä tietokantaa on muokattu niin,
MEETING PEOPLE COMMUNICATIVE QUESTIONS
 Tiistilän koulu English Grades 7-9 Heikki Raevaara MEETING PEOPLE COMMUNICATIVE QUESTIONS Meeting People Hello! Hi! Good morning! Good afternoon! How do you do? Nice to meet you. / Pleased to meet you.
Tiistilän koulu English Grades 7-9 Heikki Raevaara MEETING PEOPLE COMMUNICATIVE QUESTIONS Meeting People Hello! Hi! Good morning! Good afternoon! How do you do? Nice to meet you. / Pleased to meet you.
S SÄHKÖTEKNIIKKA JA ELEKTRONIIKKA
 S-55.00 SÄHKÖTKNKK LKTRONKK. välikoe 0.3.006. Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään!. Laske jännite U. R = =Ω, R 3 =3Ω, = =4V, 3 =6V, = + R + R 3 + U 3. Konkka on varautunut jännitteeseen u C (0) =. Kytkin
S-55.00 SÄHKÖTKNKK LKTRONKK. välikoe 0.3.006. Saat vastata vain neljään tehtävään!. Laske jännite U. R = =Ω, R 3 =3Ω, = =4V, 3 =6V, = + R + R 3 + U 3. Konkka on varautunut jännitteeseen u C (0) =. Kytkin
MUSEOT KULTTUURIPALVELUINA
 Elina Arola MUSEOT KULTTUURIPALVELUINA Tutkimuskohteena Mikkelin museot Opinnäytetyö Kulttuuripalvelujen koulutusohjelma Marraskuu 2005 KUVAILULEHTI Opinnäytetyön päivämäärä 25.11.2005 Tekijä(t) Elina
Elina Arola MUSEOT KULTTUURIPALVELUINA Tutkimuskohteena Mikkelin museot Opinnäytetyö Kulttuuripalvelujen koulutusohjelma Marraskuu 2005 KUVAILULEHTI Opinnäytetyön päivämäärä 25.11.2005 Tekijä(t) Elina
11. Models With Restricted Multipliers Assurance Region Method
 . Models With Restricted Mltipliers Assrance Region Method Kimmo Krki 3..27 Esitelmä - Kimmo Krki Contents Introdction to Models With Restricted Mltipliers (Ch 6.) Assrance region method (Ch 6.2) Formlation
. Models With Restricted Mltipliers Assrance Region Method Kimmo Krki 3..27 Esitelmä - Kimmo Krki Contents Introdction to Models With Restricted Mltipliers (Ch 6.) Assrance region method (Ch 6.2) Formlation
toukokuu 2011: Lukion kokeiden kehittämistyöryhmien suunnittelukokous
 Tuula Sutela toukokuu 2011: Lukion kokeiden kehittämistyöryhmien suunnittelukokous äidinkieli ja kirjallisuus, modersmål och litteratur, kemia, maantiede, matematiikka, englanti käsikirjoitukset vuoden
Tuula Sutela toukokuu 2011: Lukion kokeiden kehittämistyöryhmien suunnittelukokous äidinkieli ja kirjallisuus, modersmål och litteratur, kemia, maantiede, matematiikka, englanti käsikirjoitukset vuoden
f[x i ] = f i, f[x i,..., x j ] = f[x i+1,..., x j ] f[x i,..., x j 1 ] x j x i T n+1 (x) = 2xT n (x) T n 1 (x), T 0 (x) = 1, T 1 (x) = x.
![f[x i ] = f i, f[x i,..., x j ] = f[x i+1,..., x j ] f[x i,..., x j 1 ] x j x i T n+1 (x) = 2xT n (x) T n 1 (x), T 0 (x) = 1, T 1 (x) = x. f[x i ] = f i, f[x i,..., x j ] = f[x i+1,..., x j ] f[x i,..., x j 1 ] x j x i T n+1 (x) = 2xT n (x) T n 1 (x), T 0 (x) = 1, T 1 (x) = x.](/thumbs/64/52007594.jpg) Kaavakokoelma f[x i ] = f i, f[x i,..., x j ] = f[x i+,..., x j ] f[x i,..., x j ] x j x i T n+ (x) = 2xT n (x) T n (x), T (x) =, T (x) = x. n I,n = h f(t i + h 2 ), E,n = h2 (b a) f (2) (ξ). 24 i= I,n
Kaavakokoelma f[x i ] = f i, f[x i,..., x j ] = f[x i+,..., x j ] f[x i,..., x j ] x j x i T n+ (x) = 2xT n (x) T n (x), T (x) =, T (x) = x. n I,n = h f(t i + h 2 ), E,n = h2 (b a) f (2) (ξ). 24 i= I,n
Salasanan vaihto uuteen / How to change password
 Salasanan vaihto uuteen / How to change password Sisällys Salasanakäytäntö / Password policy... 2 Salasanan vaihto verkkosivulla / Change password on website... 3 Salasanan vaihto matkapuhelimella / Change
Salasanan vaihto uuteen / How to change password Sisällys Salasanakäytäntö / Password policy... 2 Salasanan vaihto verkkosivulla / Change password on website... 3 Salasanan vaihto matkapuhelimella / Change
SELL Student Games kansainvälinen opiskelijaurheilutapahtuma
 SELL Student Games kansainvälinen opiskelijaurheilutapahtuma Painonnosto 13.5.2016 (kansallinen, CUP) Below in English Paikka: Nääshalli Näsijärvenkatu 8 33210 Tampere Alustava aikataulu: Punnitus 12:00-13:00
SELL Student Games kansainvälinen opiskelijaurheilutapahtuma Painonnosto 13.5.2016 (kansallinen, CUP) Below in English Paikka: Nääshalli Näsijärvenkatu 8 33210 Tampere Alustava aikataulu: Punnitus 12:00-13:00
